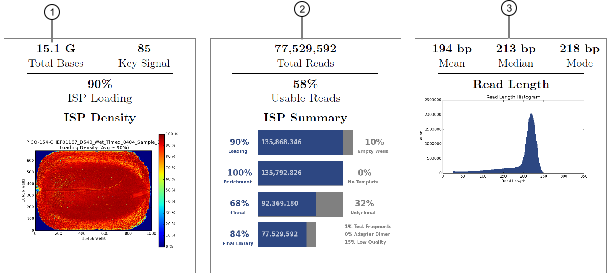
Throughput considerations
To assess a run, examine the throughput or total bases. Consider whether these numbers make sense for the application and chip type.
|
Chip type |
Number of addressable wells |
Number of reads |
Throughput |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
200 Base Read |
400 Base Read |
|||
|
~6 million |
2–3 million |
0.3–0.5 Gb |
0.6–1 Gb |
|
|
~12 million |
4–6 million |
0.6–1 Gb |
1.2–2 Gb |
|
|
~37 million |
15–20 million |
3–4 Gb |
6–8 Gb |
|
|
~150 million |
60–80 million |
10–15 Gb |
N/A |
|
|
~260 million |
100–130 million |
20–25 Gb |
N/A |
|
The following table provides information regarding the number of wells per chip type and sequencing throughput specifications for sequencing runs from an Ion PGM™ System.
|
Chip type |
Number of addressable wells |
Number of reads |
Throughput[1] |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
200 Base Read |
400 Base Read |
|||
|
~1.2 Million |
400–500 Thousand |
30–50 Mb |
60–100 Mb |
|
|
~6 Million |
2–3 Million |
300–600 Mb |
600 Mb–1 Gb |
|
|
~11 Million |
4–5.5 Million |
600 Mb–1Gb |
1.2–2 Gb |
|
The throughput, total bases, and read length metrics are found at the top of the run report. This example is from the 200-base read run (500 flows) on an Ion 540™ Chip with a CEPH control library.